Python if else Statments
If-else is the decision making statements in Python programming language similar to any other programming. Where execution of a block of statement is decided based on the result of if condition. If it evaluates a condition to true, then if block code is executed, on the false condition, the else block code is executed, which is optional.
Basically, there are 4 types of if statements.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- else-if ladder statement
- nested if statement
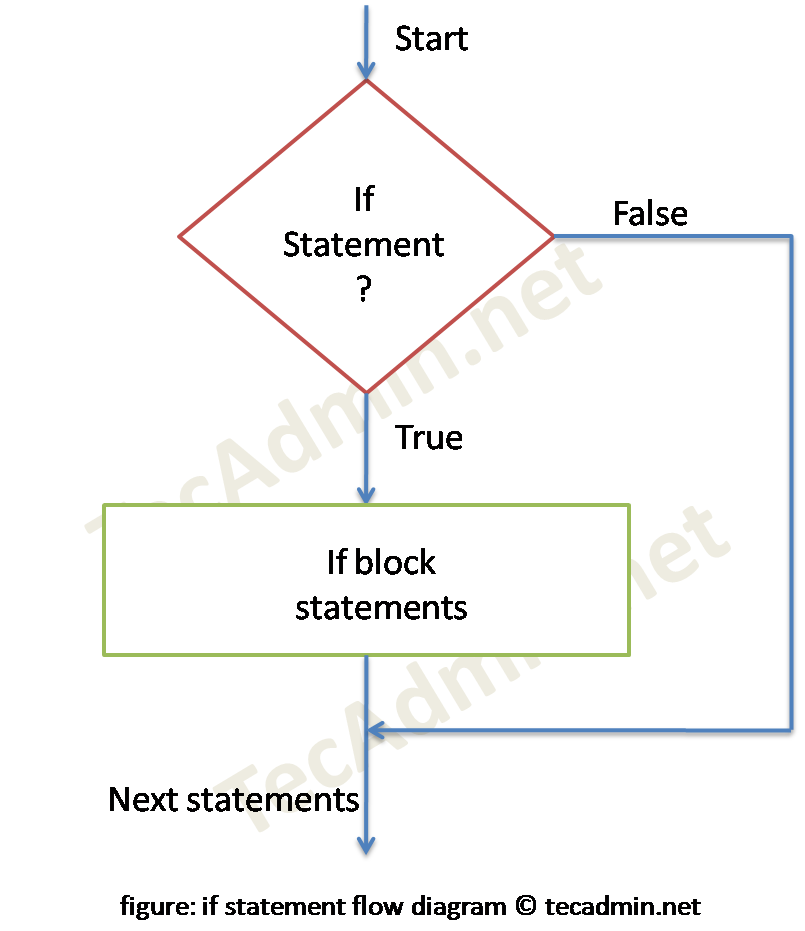
1. Python – if Statement Example
This is simple if condition, where a block of statements are executed if an expression evaluates to true. For the false condition program simply skips the statements inside if block.
Syntax:
if test expression:
statement(s)
Example:
For example, check if a person is eligible to vote. Assuming a person can vote only if his/her age is 18 or above.
Take the input from user and check eligibility:
1 2 3 | age = input("Enter your age: ") if age >= 18: print("Yes, you are eligible to vote") |
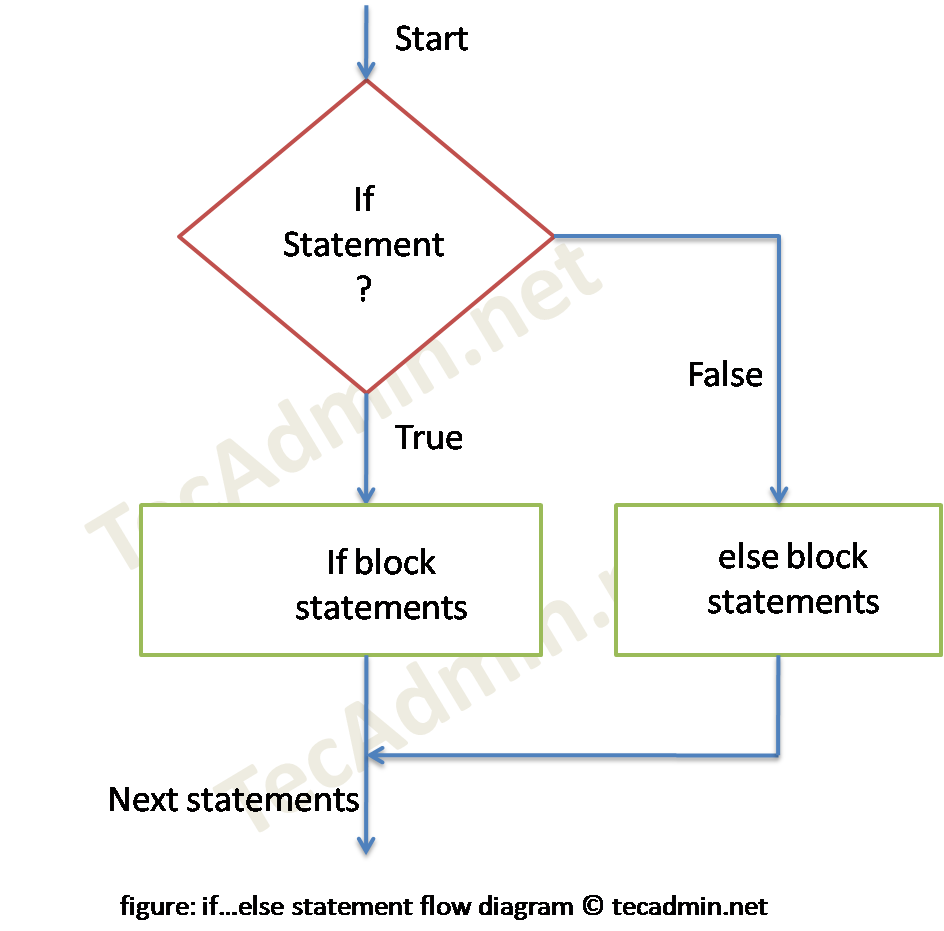
2. Python – if-else Statement Example
In case the condition evaluates to false then else is defined, then else block statements are executed (if available).
Syntax:
if test expression:
If block statement(s)
else:
Else block statement(s)
Example:
Continue with above example where we also print message if a user is not eligible to vote.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | age = input("Enter your age: ") if age >= 18: print("Yes, you are eligible to vote") else: print("Sorry, you are not eligible to vote") |
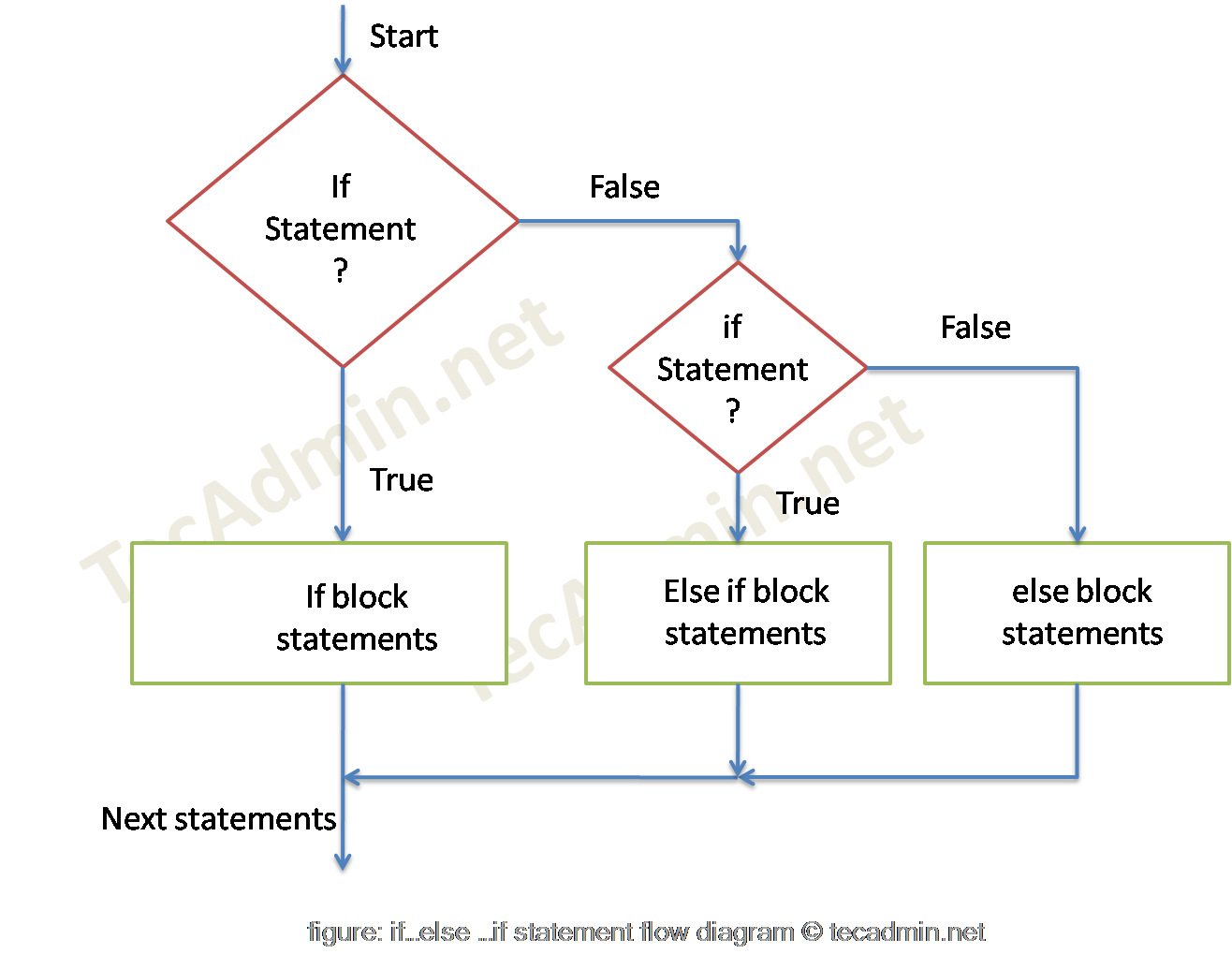
3. Python – If-elif-else Statement Example
In addition to else-if, we can check for new conditions, if the program goes to else block.
Syntax:
if test expression:
If block statement(s)
elif test expression:
Else if block statement(s)
else:
Else block statement(s)
Example:
The elif (else if) is used for multiple if conditions. In case one if the condition goes false then check another if conditions.
For example, input the marks of a student and check if marks are greater or equal to 80 then print “Very Good”.
If marks are less than 80 and greater or equal to 50 then print “Good”.
Otherwise, if marks are below 50, print “Average”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | # Run this program with multiple # values of variable num to check results marks = input("Enter your marks: ") if num >= 80: print("Very Good") elif num >= 50: print("Good") else: print("Average") |
4. Python – Nested if Statement Example
With nested if one condition goes true then only check another condition. For example, take 3 numeric values as input and check the greatest value.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | # Take three numeric value input from the user # and find out the greatest number out of three i = float(input("Enter value of i : ")) j = float(input("Enter value of j : ")) k = float(input("Enter value of k : ")) if i > j: if i > k: print("i is gretest") else print("k is gretest") elif j > k: echo "j is greatest" else: echo "k is greatest" |